Top 10 Best LCD Display Modules for Your Electronics Projects?
When embarking on electronics projects, selecting the right lcd display module is crucial. These modules provide visual output, enhancing user interaction. With so many options available, choosing the best one can be overwhelming.
In this guide, we explore the top 10 lcd display modules that stand out in functionality and design. Each module presents unique features that cater to various project needs. Some offer bold graphics, while others excel in energy efficiency.
However, navigating through specifications can be tricky. It’s easy to get lost in technical jargon. Many may overlook the balance between price and performance. Remember, the perfect lcd display module may not exist for everyone. Evaluate your project's requirements carefully to make the best choice.

Top Features to Consider in Selecting LCD Display Modules
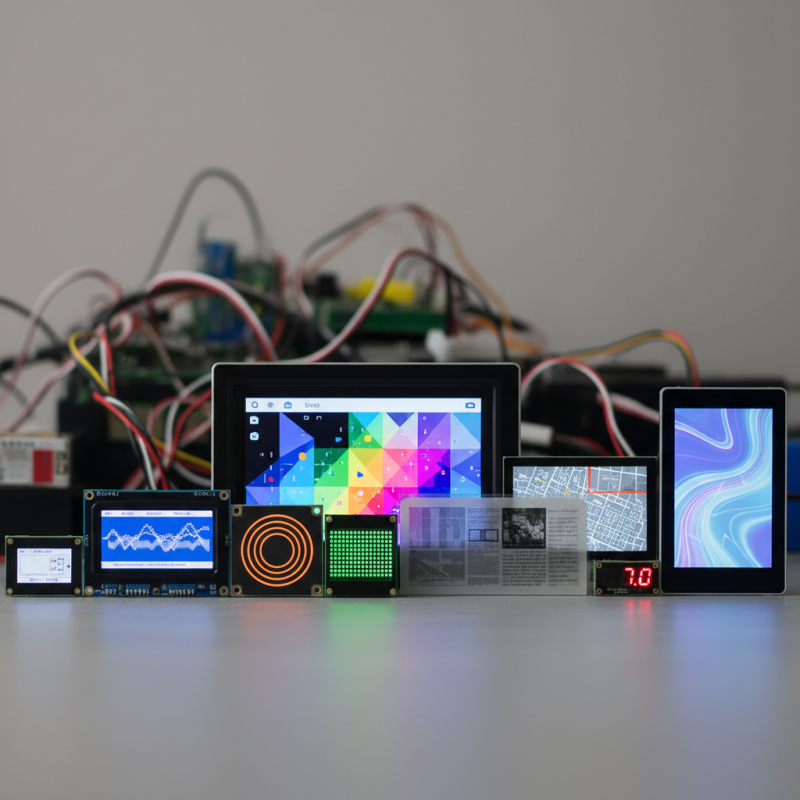
When choosing an LCD display module, several features stand out. Screen size is crucial. It determines how much information you can display at once. A larger screen is easier to read but may not fit in compact projects. Resolution also matters. Higher resolutions provide clearer images but often consume more power. This trade-off can impact battery-operated projects.
Another important aspect is the interface. Check if it suits your microcontroller. Popular options include I2C and SPI. Some modules come with built-in libraries, making integration simpler. Backlight options are also worth considering. Brightness can vary significantly. A bright display is ideal for outdoor use but drains battery faster.
Be mindful of the viewing angle too. Some displays look washed out when viewed from the side. Others maintain color integrity, enhancing flexibility in project design. Lastly, remember to evaluate the cost. High-quality modules may cost more but can save time and frustration. Choosing the right display is not just about features but also about your specific project needs. Reflection on your requirements can lead to smarter decisions.
Top 10 Best LCD Display Modules for Your Electronics Projects
This chart displays the key features of the top 10 LCD display modules evaluated for electronics projects. Each feature is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, providing a quick reference for selecting the most suitable module for your needs.
Comparison of Popular LCD Technologies: TN, IPS, and VA Panels
When choosing an LCD display for electronics projects, understanding LCD technologies is vital. TN (Twisted Nematic) panels are common due to their low cost. However, they often sacrifice viewing angles and color fidelity. In contrast, IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels offer wider viewing angles and more accurate colors. This makes them ideal for applications that require visual clarity. VA (Vertical Alignment) panels provide excellent contrast ratios. Yet, they fall behind IPS in color reproduction.
Tips: When selecting a display, consider your project’s specific needs. For vibrant graphics, IPS is preferable. If cost is a priority, TN can suffice, but be aware of its limitations.
Visuals play a critical role in user interface design. The type of LCD can influence user experience significantly. Projects demanding detailed visuals or touch sensitivity could struggle with TN displays. It is essential to weigh these factors during the decision-making process. Watch out for reflections when using glossy screens in well-lit environments.
Choosing the right LCD isn't always straightforward. Sometimes, you might overlook essential features by focusing only on price. Avoid this pitfall! Assess everything from color accuracy to response time for optimal outcomes.
Evaluating Resolution and Pixel Density in LCD Display Quality
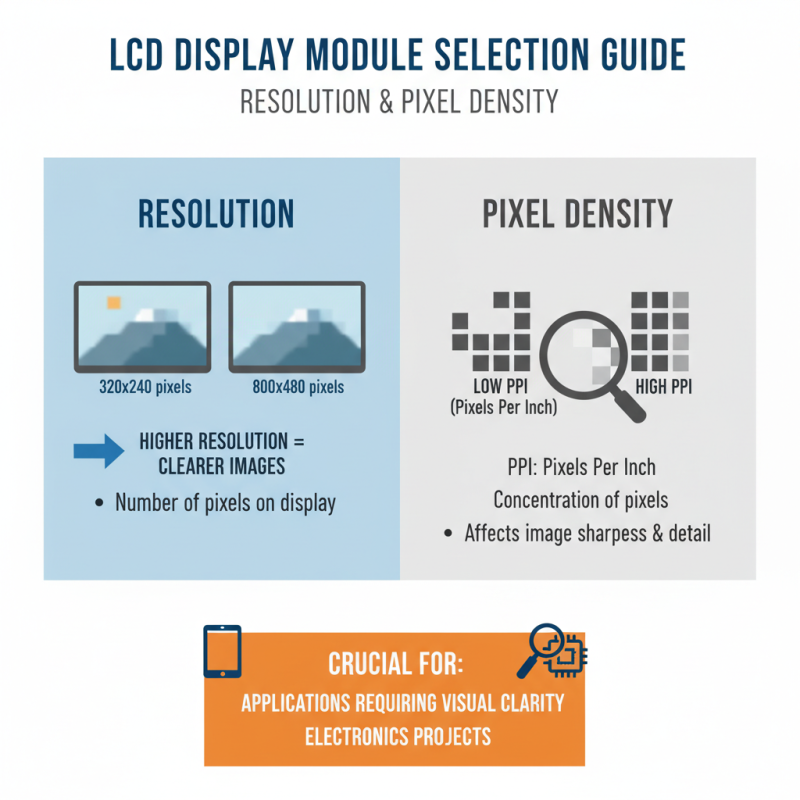
When selecting an LCD display module for your electronics projects, resolution and pixel density are crucial factors. Resolution refers to the number of pixels that make up the display. A higher resolution often leads to clearer images and better detail. For instance, a module with 800x480 pixels will present a sharper image than one with just 320x240 pixels. This distinction is vital for applications where display quality is essential.
Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), impacts how crisp and vibrant your visuals appear. A higher PPI means more detail in the same physical space. It’s not uncommon to find displays with the same resolution, but different sizes. A smaller screen with high resolution may offer more clarity compared to a larger screen with the same pixel count. However, engineers sometimes overlook PPI, focusing solely on resolution, which can lead to unsatisfactory results.
Reflect on your project's needs. Will high resolution transform user experience? Are you prepared to cope with increased cost and power usage? Many DIY enthusiasts often underestimate the importance of a good display. Poor choices may lead to frustrating user interactions. Balancing these factors is not always straightforward and requires careful consideration.
Key Use Cases for LCD Modules in Electronics Projects
LCD modules are essential components in many electronics projects. They provide a clear interface for displaying information. For hobbyists and engineers alike, they offer numerous use cases. One common application is in DIY weather stations. Here, an LCD can show temperature and humidity data in real time. This setup requires careful calibration to ensure accurate readings.
Another interesting use case is in home automation systems. Users can create control panels to manage devices like lights and fans. An LCD can provide status updates for each device. However, sometimes the readability can be an issue in bright light, which needs attention. Despite these challenges, integrating an LCD makes projects visually appealing.
Additionally, LCD modules can be used in gaming consoles. They enhance user experiences by displaying scores, levels, or game stats. Yet, designing a user-friendly interface is crucial. If the layout is crowded or confusing, players may struggle. So, careful planning and testing are vital. Adjustments along the way can lead to significant improvements.
Top 10 Best LCD Display Modules for Your Electronics Projects
| Module Type | Display Size (inches) | Resolution | Interface | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character LCD | 2x16 | 16x2 Characters | I2C, SPI | Basic Data Display |
| Graphic LCD | 2.4 | 240x320 | Parallel, SPI | User Interfaces, Charts |
| TFT LCD | 3.5 | 480x320 | SPI | Interactive Displays |
| OLED Display | 1.3 | 128x128 | I2C, SPI | Low Power Applications |
| Segmented LCD | 4.0 | Multiple Segments | Parallel | Data Representation |
| Smart LCD | 2.8 | 240x320 | UART, SPI | Vintage Projects |
| Industrial LCD | 7.0 | 800x480 | HDMI, VGA | Monitoring Systems |
| Matrix LCD | 5x7 | 35x7 Pixels | Parallel | LED Animations |
| Custom Graphics LCD | 3.2 | 320x240 | SPI, Parallel | Game Interfaces |
| Touchscreen LCD | 5.0 | 800x480 | USB, SPI | Interactive Interfaces |
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for High-Quality LCD Display Modules
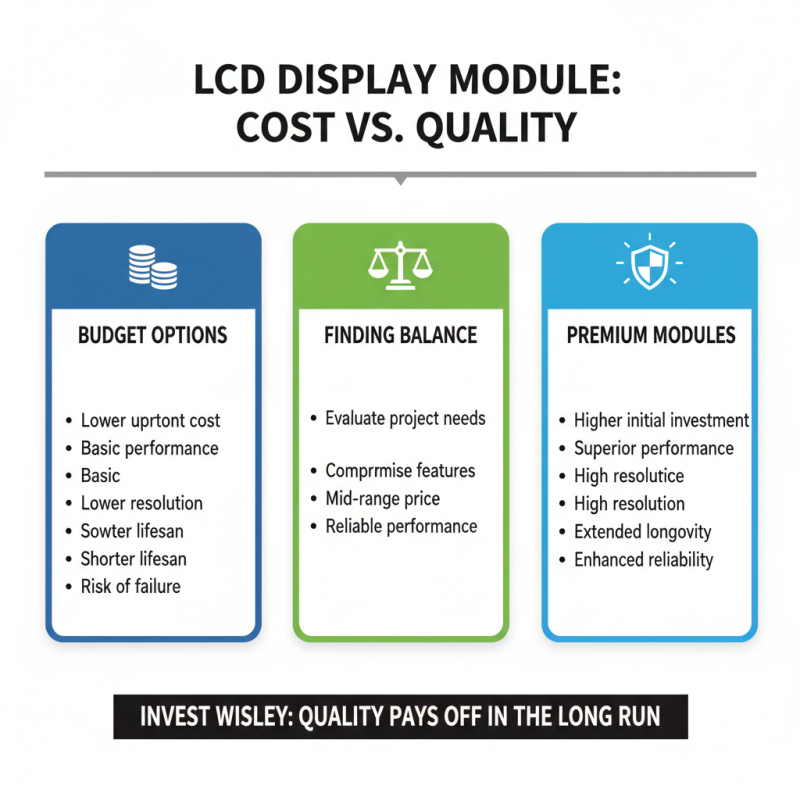
Selecting the right LCD display module for your project requires careful consideration of costs. High-quality modules often come with a hefty price tag. However, cheaper options might not deliver the performance you need. Finding the balance between cost and quality is essential. Sometimes, spending slightly more can yield significant benefits in resolution and longevity.
Budgeting efficiently is crucial. Start by determining your project requirements. Are you prioritizing size, brightness, or resolution? Next, compare various modules within your budget. You may find that certain features, like touchscreen capabilities or backlighting, can drive up costs. It's vital to avoid impulse purchases. Sometimes, features that sound appealing may not be necessary for your project.
Take a moment to reflect on your choices. Is it worth skimping on a display that might fail? Or will that extra investment pay off in the long run? These questions arise during the selection process. Understand that quality often reflects in price. However, some hidden gems offer great functionality without breaking the bank. In the end, informed decisions lead to successful projects.
Related Posts
-
Why Choose LCD Module for Your Display Needs?
-
Why Choose an LCD Display Module for Your Next Project
-

What is an LCD Display Module and How Does It Work in Electronic Devices
-

How to Choose the Best Mini LCD Display for Your Project
-

2025 How to Choose the Best LED Display for Your Business Needs
-

Top 10 LED Display Modules: Features, Prices, and Buyer’s Guide
