What is an LCD Display Module and How Does It Work in Electronic Devices
In the realm of electronic devices, the importance of an LCD display module cannot be overstated. As a pivotal component in various applications, from smartphones to industrial equipment, these modules serve as the primary interface through which users interact with technology. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in display technologies, once stated, "The LCD display module is not just a screen; it's the gateway to digital interaction, shaping how we perceive and engage with our devices."
An LCD display module consists of several key elements, including a liquid crystal layer, polarizers, and a backlight, all working in unison to produce clear, vibrant images. By manipulating light and utilizing liquid crystals, these modules can display intricate graphics and text, making them essential for user interfaces across multiple industries. As we delve deeper into the mechanics and applications of LCD display modules, it becomes evident that they are integral to advancing user experience and fostering innovation in electronic devices. Understanding how these modules operate opens the door to appreciating their impact on technology as we know it today.

What is an LCD Display Module?
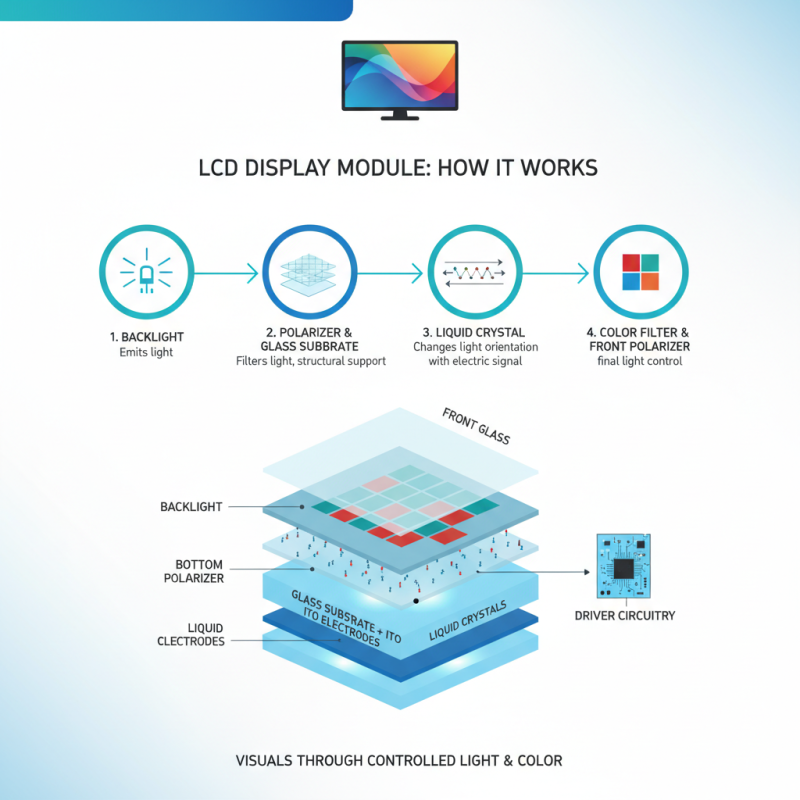
An LCD display module is a complex assembly designed to present visual information through the manipulation of light and color. LCD, or Liquid Crystal Display, relies on liquid crystals and polarizers to create images and text by controlling the light that passes through them. The core components of an LCD display module include the liquid crystal layer, backlight, driver circuitry, and glass substrate. By adjusting the orientation of the liquid crystals in response to electrical signals, the module can change the intensity and color of light to display various images.
These modules are widely used in various electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and televisions, due to their ability to produce high-quality images while being energy efficient. The backlight typically consists of LEDs that illuminate the liquid crystal layer, allowing for bright and vivid displays. The driver circuitry is crucial as it converts the digital signals from an electronic device’s processor into analog signals that dictate the behavior of the liquid crystals. This process ensures accurate and dynamic representation of images, making LCD display modules indispensable in modern electronic applications.
The Components of an LCD Display Module
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) module is an essential component used in a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones to televisions. Understanding its structure is crucial to grasp how it operates. An LCD module typically comprises several key components: a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between two glass substrates, polarizers, a backlight unit, and an electrode layer. The liquid crystals themselves are the core element that modulates light to produce images. When an electric current is applied, the orientation of the liquid crystals changes, allowing varying amounts of light to pass through, thus forming visible characters or images.
In addition to these primary elements, the LCD module often includes integrated circuits that manage the display's operations, converting the data into a visual format. According to industry reports by IHS Markit, the global LCD market was valued at approximately $135 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow as the demand for high-definition displays increases. This growth is largely driven by innovations in display technologies, enhancing brightness and viewing angles, which are critical for user experience in portable and stationary devices alike.
Tips for enhancing the lifespan of your LCD display include maintaining optimal brightness levels, avoiding exposure to direct sunlight, and regularly cleaning the display with appropriate materials. Implementing these practices can help preserve both image quality and overall functionality, ensuring that the display continues to perform effectively over time.
What is an LCD Display Module and How Does It Work in Electronic Devices
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) | A flat-panel display technology that uses liquid crystals to produce images. | Manipulates light to create images through pixel arrangement. |
| Backlight | Light source behind the LCD panel, typically LED. | Illuminates the display for visibility. |
| Driver IC | Integrated circuit that controls the LCD operations. | Converts digital signals to control the display pixels. |
| Polarizer | Filter that only allows certain light waves to pass through. | Enhances contrast and visibility of the display. |
| Glass Substrate | Transparent layer that supports the liquid crystal layer. | Holds the structure and protects the electronics inside. |
How LCD Technology Works: A Detailed Overview
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology has become a cornerstone in various electronic devices, from televisions to smartphones. At its core, LCD technology operates by manipulating light using liquid crystals, which do not emit light themselves. Instead, they modulate the light supplied by a backlight, typically a fluorescent or LED source. This modulation is achieved by applying varying electrical currents to the liquid crystals, causing them to align differently and thereby altering the light's passage through the display.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global LCD display market is expected to reach $108.8 billion by 2025, reflecting its extensive adoption across consumer electronics and other sectors. The technology primarily relies on a polarizing filter coupled with the liquid crystal layer, where the arrangement of the crystals changes based on the electrical input. This results in brightness and color variations across the display, allowing for detailed images and videos. Additionally, advancements such as TFT technology have greatly enhanced the performance and resolution of LCD screens, making them increasingly efficient and visually appealing for end-users.
Recent innovations in LCD technology have also fostered developments in energy efficiency and screen durability. Reports indicate that modern LCD displays consume up to 40% less power than older models due to improved backlight technologies and better liquid crystal formulations. These ongoing improvements not only underline the importance of LCD technology in current electronic devices but also highlight its potential for advancements in future applications across diverse markets.
Applications of LCD Display Modules in Electronic Devices

LCD display modules have become a cornerstone in the landscape of electronic devices due to their versatility and efficiency. They are widely used across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive displays, industrial equipment, and medical instruments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for LCD displays is expected to reach $127 billion by 2025, driven primarily by the increasing demand for high-performance displays in smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
In consumer electronics, LCD display modules provide crisp visuals with energy efficiency, making them an ideal choice for devices like smartphones and tablets. Their applications extend beyond personal gadgets; for instance, automotive sectors utilize LCD displays for dashboards and infotainment systems, enhancing user experience while providing vital navigation and vehicle information. In industrial and medical fields, reliability and clarity are paramount, and LCDs meet these needs by delivering accurate data and vibrant imagery, essential for monitoring equipment and diagnostic tools.
Tips: When designing products that incorporate LCD display modules, consider the display's viewing angles and backlight options for optimal user experience. Investing in quality components can significantly enhance the operational lifespan of your device, ensuring better performance over time. Moreover, understanding the specific requirements of your target application, such as brightness and resolution, can lead to better product outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Using LCD Display Modules
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) modules have become a staple in a vast array of electronic devices, ranging from smartphones to industrial equipment. One of the primary advantages of LCD display modules is their energy efficiency. According to a report by the International Display Research (IDR), LCDs consume up to 50% less power compared to traditional CRT displays. This energy efficiency makes them ideal for battery-operated devices, extending operational time and reducing overall energy costs.
However, LCD modules are not without their limitations. For instance, their response time is generally slower than that of their OLED counterparts, which can lead to motion blur in fast-moving images. An industry study published in the Journal of Display Technology highlights that while LCDs can achieve a response time of around 8 ms, OLED displays boast speeds lower than 1 ms, making them preferable for applications demanding high refresh rates, such as gaming and high-definition video playback. Furthermore, the viewing angles of LCDs are limited, resulting in color distortion when viewed from the side, while newer technologies like IPS LCDs attempt to address this issue but often at a higher manufacturing cost.
In summary, while LCD display modules offer significant advantages like energy efficiency and lower costs, their limitations regarding response time and viewing angles could impact their suitability for certain applications, as noted by various industry analysts. Hence, choosing the right display technology requires careful consideration of these factors based on the specific needs of the application.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 LED Display Modules: Features, Prices, and Buyer’s Guide
-

2025 How to Choose the Best High Brightness LCD Display for Your Needs
-

10 Best Mini LCD Displays for Your Next Project
-
Why Choose an LCD Display Module for Your Next Project
-

What is an LCD Screen? Understanding Types, Features, and Uses Explained
-

2025 Top 10 Mini LCD Displays You Should Consider for Your Setup
