What is an LCD Screen? Understanding Types, Features, and Uses Explained
As the demand for high-quality visual displays continues to rise across various industries, understanding the intricacies of LCD screens has become increasingly essential. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global LCD screen market was valued at approximately $133.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow significantly over the next decade. This surge in demand is driven by the proliferation of LCD technology in sectors such as consumer electronics, healthcare, and automotive, making it crucial for industry professionals and consumers alike to grasp the types, features, and applications of LCD screens.
Dr. Emily Harris, a leading expert in display technology and author of several industry publications, emphasizes the importance of understanding LCD screens in her statement: "The evolution of LCD technology has revolutionized how we interact with digital content, making it vital for us to stay informed about its advancements and applications." By exploring different types of LCD screens and their various features, we can appreciate their role in enhancing visual experiences while navigating new innovations on the horizon. This exploration not only helps consumers make informed decisions but also aids manufacturers in meeting the diverse needs of the market.

What is an LCD Screen? A Comprehensive Overview
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen is an advanced display technology that utilizes liquid crystals to produce images. These screens have become ubiquitous in various devices, including televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones, due to their slim profile and energy efficiency. At the core of an LCD screen is a layer of liquid crystals sandwiched between two panels of glass or plastic. When an electrical current passes through the crystals, they align to control the passage of light, which creates images by modulating the backlight.
LCD screens come in various types, including Twisted Nematic (TN), In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Vertical Alignment (VA), each offering distinct advantages in terms of color reproduction, viewing angles, and response times. TN panels are known for their fast response times, making them ideal for gaming, while IPS panels provide superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles, preferred for tasks that demand precise visuals, such as graphic design.
Furthermore, LCD technology is also adaptive, with features like touchscreen capabilities and high-definition resolutions enhancing user interaction and experience across a multitude of applications.
Types of LCD Screens: Comparison of TN, IPS, and VA Panels
When exploring the types of LCD screens, it's essential to understand the differences between TN (Twisted Nematic), IPS (In-Plane Switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment) panels, as each offers distinct advantages tailored to varied user needs. TN panels are known for their faster response times, making them a popular choice for competitive gaming; however, they typically suffer from poorer color reproduction and limited viewing angles compared to their counterparts. Reports indicate that TN technology holds approximately 35% of the market share due to its affordability and efficient performance in dynamic visual settings.
On the other hand, IPS panels offer superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for graphic design and professional photography. According to industry research by IHS Markit, IPS displays account for about 25% of the global market, with their growing popularity attributed to advancements in color fidelity and consistency. While IPS panels may have slower response times than TN panels, technological developments have bridged the gap considerably.
VA panels provide an appealing middle ground, boasting deep blacks and high contrast ratios, which enhance the viewing experience for movies and games in dark environments. Their market share, currently around 20% according to Market Research Future, is gaining traction as they balance performance and image quality.
**Tips:** When choosing an LCD screen, consider the primary use—gaming, professional work, or casual viewing—as this will significantly influence your experience. Always check the specifications for response times, color accuracy, and viewing angles to ensure the selected panel meets your needs. If budget allows, consider testing the panels physically to ascertain visual preference before making a purchase decision.
Key Features of LCD Screens: Resolution, Refresh Rate, and Contrast Ratio
When discussing LCD screens, three key features stand out: resolution, refresh rate, and contrast ratio. Resolution refers to the number of pixels displayed on the screen, which directly impacts the clarity and detail of the image. Higher resolutions, such as Full HD or 4K, allow for more intricate visuals, making them ideal for applications that demand precision, such as graphic design and video editing. As the resolution increases, so does the ability to display finer details, resulting in a more immersive viewing experience.
The refresh rate complements resolution by determining how often the screen updates the displayed image per second. Measured in hertz (Hz), a higher refresh rate leads to smoother motion portrayal, which is particularly beneficial in fast-paced scenarios like gaming or sports broadcasting. For instance, a screen with a refresh rate of 60Hz showcases an adequate performance for most everyday applications, while 120Hz or higher is preferred for gamers seeking fluid visuals and reduced motion blur.
Lastly, the contrast ratio is crucial for assessing the depth of colors and the ability of a screen to display dark and bright images effectively. A higher contrast ratio results in deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, enhancing overall image quality. This feature is especially significant in environments with varying light conditions, as it ensures that the screen remains legible and aesthetically pleasing, whether viewing in dim light or direct sunlight. Understanding these key aspects helps users select LCD screens that best suit their needs, ensuring an optimal viewing experience.
Applications of LCD Screens in Consumer Electronics and Industrial Uses
LCD screens, or Liquid Crystal Displays, have become integral components in both consumer electronics and industrial applications. In the realm of consumer devices, LCD technology is primarily utilized in televisions, computer monitors, smartphones, and tablets. Their lightweight design and ability to produce high-quality images with vivid colors have made them incredibly popular. Moreover, the thin profile of LCD screens allows for sleek device designs, which cater to modern aesthetics without compromising on functionality. The versatility of these displays has also enabled advancements in screen sizes, offering options from compact screens for portable devices to large panels for immersive viewing experiences.
In industrial settings, LCD screens serve critical roles in various applications, including control panels, medical equipment, and signage. Their robustness and ability to function in diverse environmental conditions make them suitable for use in factories and outdoor settings. For instance, LCDs can provide real-time data in manufacturing processes, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Additionally, in the medical field, LCD displays are essential for imaging and monitoring devices, offering precise visuals that aid in diagnostics and patient care. The adaptability of LCD screens enables them to meet specific requirements, whether it's durability, brightness, or integration into complex systems, showcasing their vast potential beyond consumer use.
Industry Trends: The Future of LCD Technology in Display Solutions
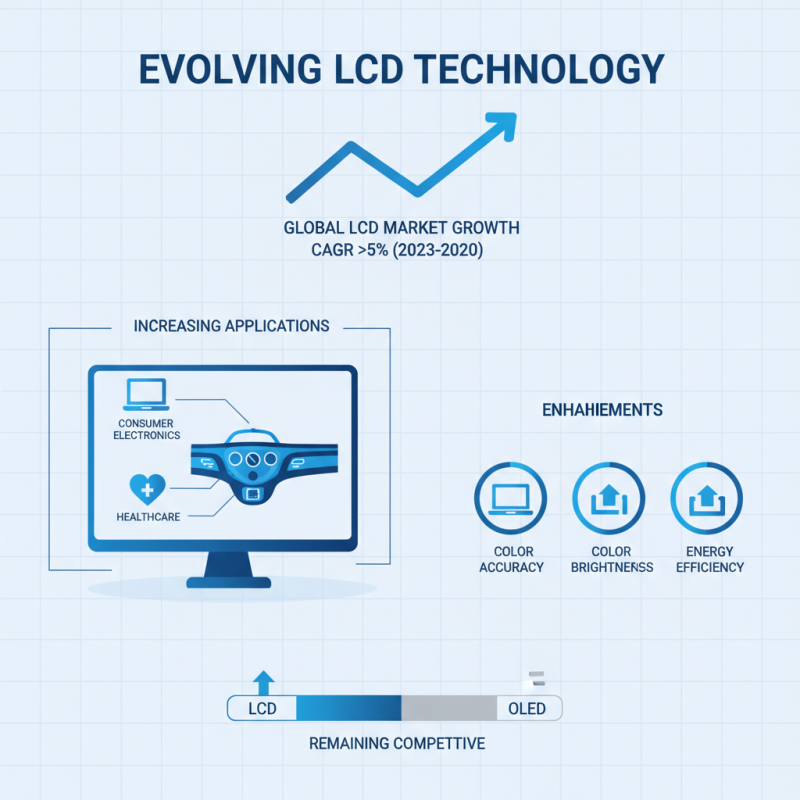
The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology continues to evolve, adapting to the demands of modern consumers and industries. Recent market reports indicate that the global LCD market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% from 2023 to 2030, driven by advancements in display technology and increasing applications in various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare. As manufacturers invest in research and development, we can expect to see enhancements in color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency, enabling LCDs to remain competitive against other technologies like OLED.
One of the key trends shaping the future of LCD technology is the transition towards higher resolution displays, such as 4K and 8K. According to industry analyses, the demand for higher resolution has surged, particularly in sectors such as gaming and professional graphic design, where display quality is paramount. Furthermore, the integration of smart features in LCD screens is on the rise, as connectivity becomes a standard expectation among users. Innovations such as improved backlighting techniques and quantum dot technology are expected to further enhance display performance, making LCDs not only versatile but also essential in the next generation of display solutions. This shift reinforces the importance of LCDs in a landscape increasingly characterized by multi-functional and high-performance display requirements.




